 As humans, our DNA consists of a unique code that forms the building blocks for who each of us is as a person – defining key traits, including our health status.
As humans, our DNA consists of a unique code that forms the building blocks for who each of us is as a person – defining key traits, including our health status.
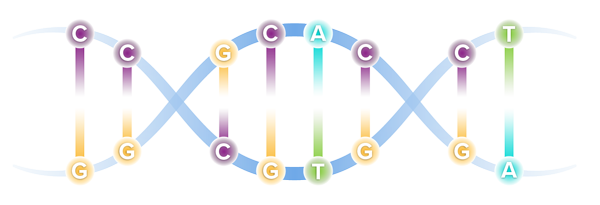
Our DNA comprises four types of bases, referred to by specific letters, that spell out our unique genetic code. The four bases are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). These bases are present in our DNA as pairs.
Though our genome comprises more than 6 billion base pairs, a single misspelling in that code, known as a point mutation, can serve as the catalyst for serious illness. Through recent genetic discoveries, companies today are leveraging gene editing technologies to address these mutations and potentially cure the underlying cause of disease.



 As humans, our DNA consists of a unique code that forms the building blocks for who each of us is as a person – defining key traits, including our health status.
As humans, our DNA consists of a unique code that forms the building blocks for who each of us is as a person – defining key traits, including our health status. 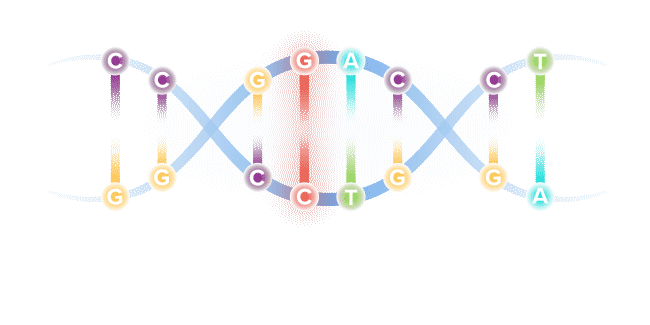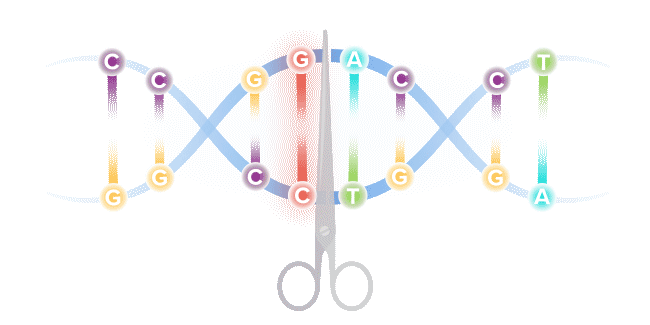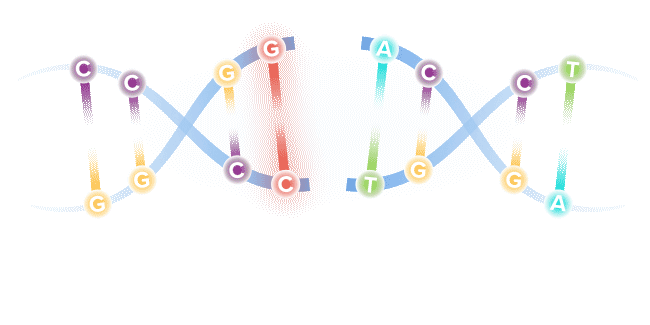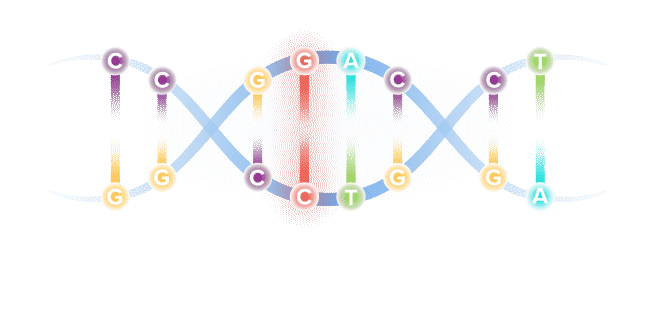
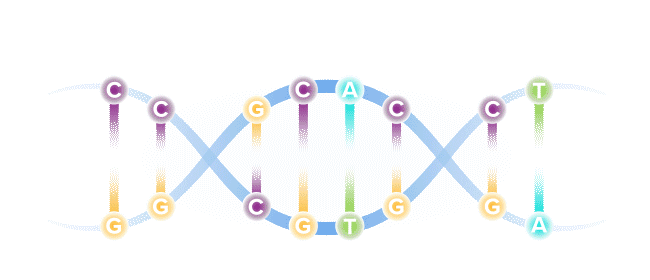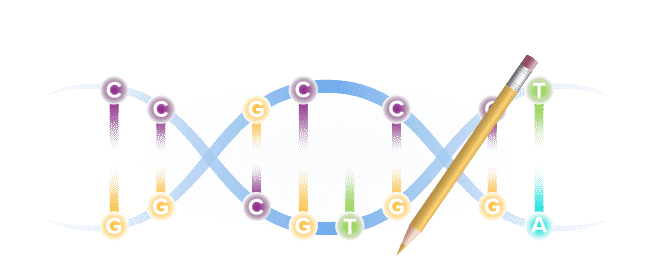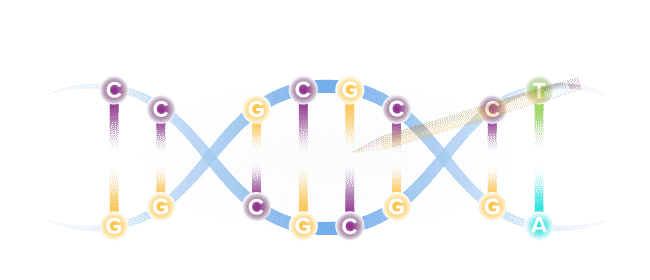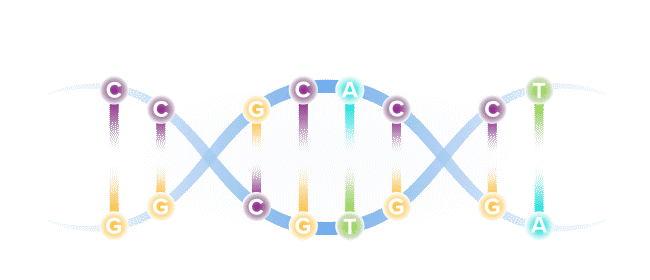 Base editing is a next-generation form of gene editing. Base editors can most simply be compared to pencils, in their ability to "erase" and rewrite a specific letter in a gene.
Base editing is a next-generation form of gene editing. Base editors can most simply be compared to pencils, in their ability to "erase" and rewrite a specific letter in a gene.